Understanding Bone Grafting in Dental procedures: A Comprehensive Guide
Enhance Your Jawbone Level With Bone Grafting!
Were you told that you do not have enough bone level to replace your missing teeth
We might be able to provide a solution to your problem. We might be able to augment your bone level by performing a procedure called bone grafting. You can’t grow new teeth, but dental implants are the next best thing. Bone grafting is a surgical technique that replaces and rebuilds diseased or damaged bones using transplanted bones.Benefits of
Bone Grafting
If you are having dental implants or not, a bone graft is recommended if you have lost teeth and your jawbone is compromised, and this operation has many advantages:
- Long after the tooth is gone, it gives us the ability to retain the bony ridge's form and strength.
- It enhances the possibility of having an implant, a bridge, a denture, or a partial placement in the future.
- It prevents shrinkage over time in the height and width of the mouth.
- It prevents the risk of the jaw structure being narrow, short, and fragile.
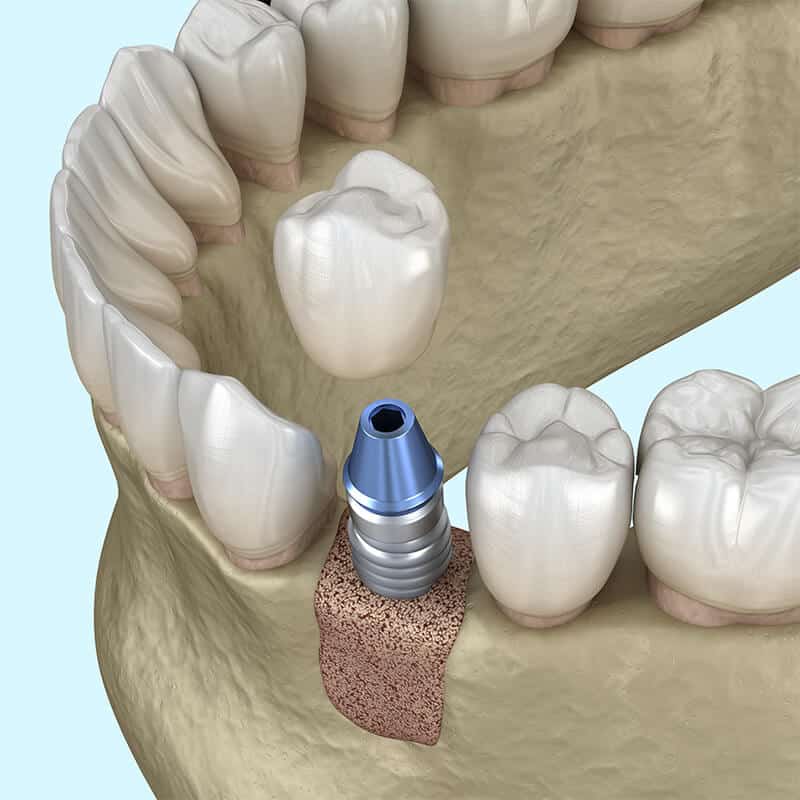
Bone Grafting Process
Ready to get started?
Reach us now to schedule your consultation
Frequently Asked Questions on Bone Grafting
What is bone grafting?
What are the types of bone grafting materials?
- Autograft is the bone of the patient itself. It is harvested mainly from the iliac crest or chin area. Since it contains living cells and human growth factors, it is the perfect bone replacement.
- Allograft bone is extracted from humans other than the individual receiving it. It can be removed from cadavers or living donors (tissue harvested from hip replacement surgery). It has the composition and structure of natural bones.
- Alloplast is a synthetically produced bone graft material from hydroxyapatite (a naturally occurring mineral) so that there is no chance of transmission of the disease. Calcium phosphate-based ceramics such as hydroxyapatite (HA) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP) are the most common alloplastic materials.
- Xenograft bone replacement originates from a non-human animal such as bovine bone (or recently porcine bone) that can be freeze-dried or demineralized and deproteinized.
Why was I recommended bone grafting?
- Missing teeth
- Periodontal diseases
- Misaligned teeth
- Support for dental implants
What is Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP)?
What are the indications of dental bone grafts?
- In the tooth socket after removal of the tooth
- Replacement of a local bone defect due to trauma or infection
- To fill a defect around the implant caused by a condition called peri-implantitis
- For increasing the height of the mandible and maxilla
- For enhancing the width of the maxilla and the mandible
How is bone grafting done?
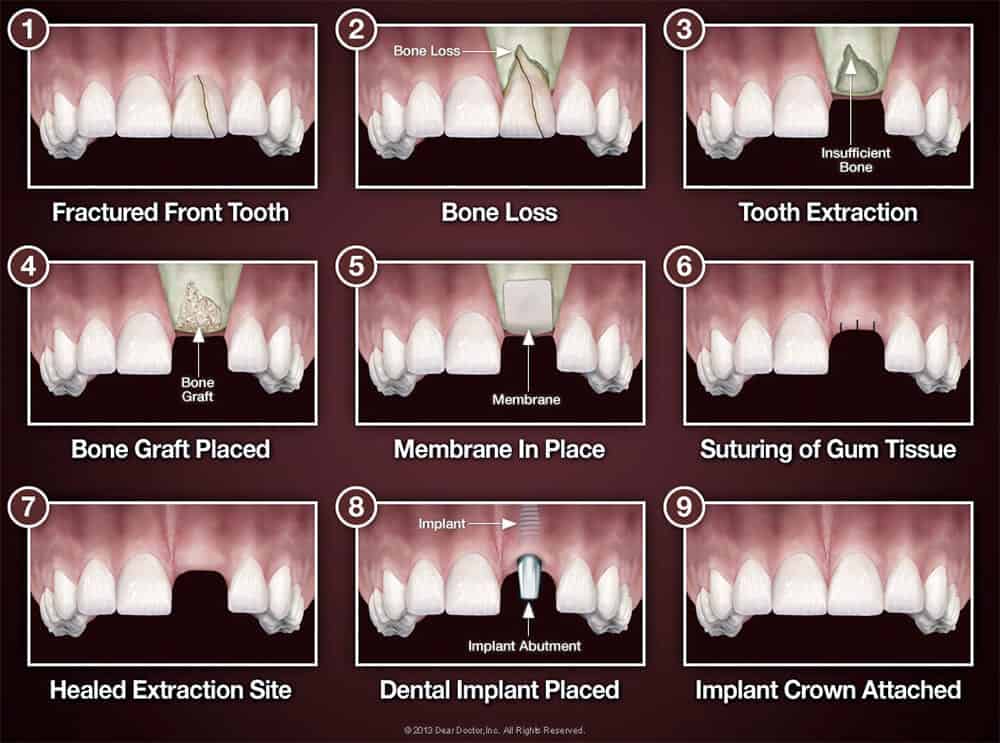
Bone grafting, usually a small surgical procedure performed in the dental office, is used to put up new bones that retain teeth in the area of your mouth. A tiny incision is made in your gum to reveal the bone underneath it, and then grafting material is applied.
The grafting material is the most frequently processed bone that acts as a scaffold, around which your body can deposit new bone cells. Your body will finally absorb the grafting material and substitute it with your new bone.
The appropriate grafting material may come from many sources. It comes from your own body sometimes. However, more frequently, it is an animal or human donor's bone treated by a laboratory to make it sterile and healthy. The grafting material may also be synthetic. It comes in many forms: powder, granules, putty, or even a gel injected with a syringe.



